Selasa, Disember 4
Sabtu, November 24
Jumaat, November 23
Language and Communication
How to cut a
copper tube with a tube cutter
1.
Place a coil
of copper tube on a worktable.
2.
Unroll the
tube.
3.
Measure the
length and use scriber to mark the copper tube for cutting.
4.
Loosen the
screw of the tube cutter.
5.
Place the
tube in ‘v’ guide of the tube cutter.
6.
Hold up the
copper tube in the left hand and the tube cutter in the right hand.
7.
Tighten the
thumb screw of the tube cutter and set blade on markings on the tube.
8.
Apply
pressure on the table.
9.
Turn the
cutter clockwise and anti-clockwise around the tube until the tube is cut.
10. Ream and file the ends of the tube.
Job title: Cutting a copper tube with a tube
cutter
Equipment/materials: a coil of copper tube , scriber , tube cutter
, file
Procedure:
First, the coil of copper tube is placed on a
worktable and unrolled. The length is measured and a scriber is
used to mark the copper tube for cutting. Next, the screw of the tube
cutter is loosened. After that, the tube is placed in the ‘v’
guide of the tube cutter.
Subsequently,
the copper tube is held up in the left hand and the tube cutter in the
right hand. In the next stage, the thumb screw of the tube cutter is
tightened and the blade is set on the marking on the tube. After
this, pressure is applied on the blade. The cutter is turned clockwise
and anti-clockwise around the tube until it is cut. Finally, the end of
the tube is reamed and filed.
Ahad, Oktober 14
Rabu, Oktober 10
Selasa, Oktober 9
Jumaat, Oktober 5
Homeworks to do
1.3 – Constructing of
Ellipse
1.3.1 – Ellipses/Ovals
An ellipse (Greek “elleipsis”
- a "falling short") is a plane curve that results
from the intersection of a cone by a plane in a way that produces a closed
curve,
(See Fig.27).
Fig.27 – An ellipse
obtained as the intersection of a cone with a plane
There are several methods
whereby an ellipse can be drawn, by given the length of its major and minor
axes:
a) The Auxiliary Circle
Method
·
Steps 1 – Draw the major axis
AB. Draw a circle by taking radius of OA from centre O.
·
Steps 2 – Draw another circle
whose diameters are the minor axis. Point CD is form by erect a perpendicular
line from O. Now A, B, C and D are points on the ellipse. The next task is to
find the position of the other points on the ellipse and then to join them
together.
·
Steps 3 – Divided those
circle into a convenient number of parts (preferably 12 parts). This can be
easily done using the 30°/60° set square.
·
Steps 4 – Draw horizontal and
vertical lines at where the big circle and small circle met with the 12 parts
line. The intersection of the horizontal and vertical line becomes a point on
the ellipse.
·
Steps 5 – Plot all those
point together to draw the ellipse. This can be done with “French curve” or
“Flexible curve” or “Freehand” method.
b) The Rectangle
Method/Radial Line Method
·
Steps 1 – Draw the major axes
AB and minor axes CD respectively, intersecting at O.
·
Steps 2 – Produce a rectangle
by drawing EF and GH both parallel to AB, and EG and FH parallel to CD
respectively.
·
Steps 3 – Divided OA and OB
into the same number of equal parts (preferably 4 parts) and numbering the
points 1,2,3 and 4 as shown. This can be done by using “division of line
method”.
·
Steps 4 – Draw radial line
from D and C through point 1, 2, 3 and 4 on line OA and OB.
·
Steps 5 – Divided AE, AG, BF
and BH into the same number of equal parts (preferably 4 parts) and numbering
the points 1,2,3 and 4 as shown. This can be done by using “division of line
method”.
·
Steps 6 – Draw radial line
from D and C through point 1, 2, 3 and 4 on line AE, AG, BF and BH. The intersection
of the above line becomes a point on the ellipse.
·
Steps 7 – Plot all those
points together to draw the ellipse. This can be done with “French curve” or
“Flexible curve” or “Freehand” method.
c) The Four Arc Method
There are occasions when it is
not essential that an ellipse on a drawing can be shown with a great accuracy.
Although this is only approximate but it is permissible to use this method
since it can be drawn using straight edge and compasses only.
·
Steps 1 – Draw the major axes
AB and minor axes CD respectively, intersecting at O.
·
Steps 2 – Produce a rectangle
by drawing EF and GH both parallel to AB, and EG and FH parallel to CD
respectively.
·
Steps 3 – Join ED
·
Steps 4 – Bisect AE to find
point J and join JC. Point K is result from he intersecting of line JC and ED.
·
Steps 5 – Join AK and bisect
it at right angles. The bisecting line LM cuts on line AB producing point N.
·
Steps 6 – Bisect line KC at
right angles. The bisecting line PQ cuts on line CD producing point R.
·
Steps 7 – With centre R and
radius from RC, draw an arc from point C to point K.
·
Steps 8 – With centre N and
radius from NA, draw an arc from point A to point K.
·
Steps 9 – By stepping off CS
equal to DR, and BT equal to AN, we then have the four centres N, R, S and T
from which we can drawn four arcs to produce a good approximation of the
ellipse.
(Note: Only a good compass can produce a very accurate
approximation of this method.)
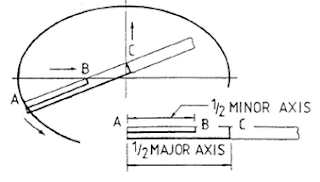
d)
The Trammel Method
·
For this method, you must have “a thick paper and a scissor”.
·
The measurements of the major and minor axis are provided.
·
The formula for this method are; Point AC = ½ of the Major Axis,
and Point AB = Minor Axis.
·
Draw a trammel on a thick paper by applying the above formula. Once
done, and then cut the trammel.
·
Trace/point out the path of the ellipse using the end of point A as a
guide. During this process, make sure that the points B and C on the trammel
must always touch the major and minor axes.
Khamis, Oktober 4
Rabu, Oktober 3
kursus fire marshall
Per: Kursus Skim Mencegah Kebakaran 2012
Tarikh: 24hb , 25hb dan 26hb September 2012Hari: Isnin hingga Rabu
Jam: 0800 pagi hingga 1200 tengahari
dan besambung 1330 petang hingga 1630 petang
Tempat: Balai Bomba Kuala Belait
Pakaian: Pakaian Sukan
Kursus Skim Mencegah Kebakaran ini terbuka kepada semua Sr dan Asr Maktab Kejuruteraan Jefri Bolkiah Kuala Belait. Kursus ini di ketuai oleh Cikgu Muhammad Khairul Hajri Haji Jahari,Fire Safety Coordinator .
Selasa, September 11
Langgan:
Ulasan (Atom)









































.jpg)






